In this unit, you will practice forming and using questions as well as negations in English.
Questions
You will focus on question words, word order, and auxiliary verbs to ask for information in different situations.
Summary:
In English, questions can be formed in different ways depending on the information you want to ask for:
1. Yes/No Questions
These questions can be answered with yes or no. They are formed by placing an auxiliary or modal verb before the subject, followed by the main verb.
Sentence Structure:
Auxiliary / Modal Verb + Subject + Main Verb
Examples:
- Do you know what a trifle is?
- Does this bowl look big enough?
- Can we start?
Common auxiliaries/modals:
- Do/does/did
- Is/are/was/were
- Have/has
- Can, will, must
2. Wh-Questions
These questions ask for specific information and start with a question word: what, where, when, who, why, which
Sentence Structure:
Wh-word + Object + Auxiliary/Modal Verb + Subject + Main Verb
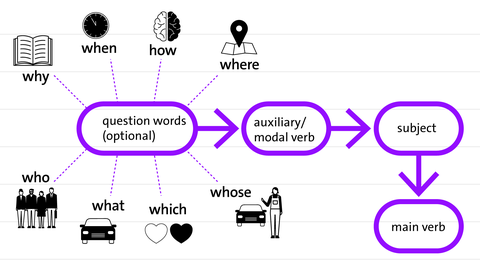
Examples:
- Which fruit would you like?
- Where are you going?
- What bowl should we use for our dessert?
2. Indirect Questions
These are polite or formal questions embedded in a statement. The word order follows a statement rather than a direct question.
Examples:
- Could you tell me what custard is?
- Do you know where my spoon is?
Negations
In the following, you will practice using negations in English. You will focus on forming negative sentences with words such as not, never, and no, and learn how negation changes meaning to make statements clearer and more precise.
Summary:
Negation in English
1. Using “not“
- Shows that a verb is negative.
- Structure: Subject + auxiliary/modal verb + “not“ + main verb
- not can also appear contracted/shortened: e.g. would not ⟹ wouldn’t
Examples:
- I can’t/cannot eat dairy.
- Salt would not be correct or tasty at all.
- Ellie usually doesn’t like cream.
2. Using “no“
- Used before a noun to show absence.
- Structure: Introductory phrase + “no” + noun
Examples:
- If you have no cream, you could skip that last part.
- There is no milk in the fridge.
3. Using “never“
- Shows that something doesn’t happen at any time.
- Structure: Subject + “never“ + verb (+ object)
Examples:
- Ellie never eats dessert.
- I have never tried a trifle before.